Init
This commit is contained in:
commit
18426c7552
10 changed files with 4725 additions and 0 deletions
17
README.md
Normal file
17
README.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
|||
## Sources
|
||||
|
||||
- [cifar10-fast-simple](https://github.com/99991/cifar10-fast-simple)
|
||||
|
||||
## Setup
|
||||
|
||||
Get miniconda [here](https://docs.anaconda.com/miniconda/install/#quick-command-line-install)
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
conda create --name mia_distilled python=3.11.2
|
||||
conda activate mia_distilled
|
||||
conda install pytorch torchvision torchaudio pytorch-cuda=12.1 -c pytorch -c nvidia
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We've found that CUDA 12.2 will still run without issue on `pytorch-cuda=12.1`.
|
||||
There is also a `pytorch-cuda=12.4`. Check your system CUDA version with
|
||||
`nvidia-smi`.
|
||||
129
cifar10-fast-simple/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
129
cifar10-fast-simple/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
|
|||
# Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
|
||||
__pycache__/
|
||||
*.py[cod]
|
||||
*$py.class
|
||||
|
||||
# C extensions
|
||||
*.so
|
||||
|
||||
# Distribution / packaging
|
||||
.Python
|
||||
build/
|
||||
develop-eggs/
|
||||
dist/
|
||||
downloads/
|
||||
eggs/
|
||||
.eggs/
|
||||
lib/
|
||||
lib64/
|
||||
parts/
|
||||
sdist/
|
||||
var/
|
||||
wheels/
|
||||
pip-wheel-metadata/
|
||||
share/python-wheels/
|
||||
*.egg-info/
|
||||
.installed.cfg
|
||||
*.egg
|
||||
MANIFEST
|
||||
|
||||
# PyInstaller
|
||||
# Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
|
||||
# before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
|
||||
*.manifest
|
||||
*.spec
|
||||
|
||||
# Installer logs
|
||||
pip-log.txt
|
||||
pip-delete-this-directory.txt
|
||||
|
||||
# Unit test / coverage reports
|
||||
htmlcov/
|
||||
.tox/
|
||||
.nox/
|
||||
.coverage
|
||||
.coverage.*
|
||||
.cache
|
||||
nosetests.xml
|
||||
coverage.xml
|
||||
*.cover
|
||||
*.py,cover
|
||||
.hypothesis/
|
||||
.pytest_cache/
|
||||
|
||||
# Translations
|
||||
*.mo
|
||||
*.pot
|
||||
|
||||
# Django stuff:
|
||||
*.log
|
||||
local_settings.py
|
||||
db.sqlite3
|
||||
db.sqlite3-journal
|
||||
|
||||
# Flask stuff:
|
||||
instance/
|
||||
.webassets-cache
|
||||
|
||||
# Scrapy stuff:
|
||||
.scrapy
|
||||
|
||||
# Sphinx documentation
|
||||
docs/_build/
|
||||
|
||||
# PyBuilder
|
||||
target/
|
||||
|
||||
# Jupyter Notebook
|
||||
.ipynb_checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
# IPython
|
||||
profile_default/
|
||||
ipython_config.py
|
||||
|
||||
# pyenv
|
||||
.python-version
|
||||
|
||||
# pipenv
|
||||
# According to pypa/pipenv#598, it is recommended to include Pipfile.lock in version control.
|
||||
# However, in case of collaboration, if having platform-specific dependencies or dependencies
|
||||
# having no cross-platform support, pipenv may install dependencies that don't work, or not
|
||||
# install all needed dependencies.
|
||||
#Pipfile.lock
|
||||
|
||||
# PEP 582; used by e.g. github.com/David-OConnor/pyflow
|
||||
__pypackages__/
|
||||
|
||||
# Celery stuff
|
||||
celerybeat-schedule
|
||||
celerybeat.pid
|
||||
|
||||
# SageMath parsed files
|
||||
*.sage.py
|
||||
|
||||
# Environments
|
||||
.env
|
||||
.venv
|
||||
env/
|
||||
venv/
|
||||
ENV/
|
||||
env.bak/
|
||||
venv.bak/
|
||||
|
||||
# Spyder project settings
|
||||
.spyderproject
|
||||
.spyproject
|
||||
|
||||
# Rope project settings
|
||||
.ropeproject
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdocs documentation
|
||||
/site
|
||||
|
||||
# mypy
|
||||
.mypy_cache/
|
||||
.dmypy.json
|
||||
dmypy.json
|
||||
|
||||
# Pyre type checker
|
||||
.pyre/
|
||||
21
cifar10-fast-simple/LICENSE
Normal file
21
cifar10-fast-simple/LICENSE
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
|||
MIT License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2021 Thomas Germer
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
99
cifar10-fast-simple/README.md
Normal file
99
cifar10-fast-simple/README.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
|||
# Description
|
||||
|
||||
This project is a simplified version of David Page's amazing blog post [How to Train Your ResNet 8: Bag of Tricks](https://myrtle.ai/learn/how-to-train-your-resnet-8-bag-of-tricks/), where a modified ResNet is trained to reach 94% accuracy in 26 seconds on a V100 GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
**Update:** Also check out https://github.com/tysam-code/hlb-CIFAR10 for even faster training!
|
||||
|
||||
# Usage
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/99991/cifar10-fast-simple.git
|
||||
cd cifar10-fast-simple
|
||||
python3 train.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# Example output
|
||||
|
||||
* Timing results using an A100 GPU only including training and excluding preprocessing and evaluation. The first run still includes some PyTorch/CuDNN initialization work and takes 15.49 sec.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
epoch batch train time [sec] validation accuracy
|
||||
1 97 1.43 0.1557
|
||||
2 194 2.86 0.7767
|
||||
3 291 4.29 0.8756
|
||||
4 388 5.73 0.8975
|
||||
5 485 7.16 0.9118
|
||||
6 582 8.59 0.9204
|
||||
7 679 10.02 0.9294
|
||||
8 776 11.45 0.9373
|
||||
9 873 12.88 0.9401
|
||||
10 970 14.32 0.9427
|
||||
|
||||
84 of 100 runs >= 94.0 % accuracy
|
||||
Min accuracy: 0.9379000000000001
|
||||
Max accuracy: 0.9438000000000001
|
||||
Mean accuracy: 0.9409949999999995 +- 0.0012262442660416419
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Epoch vs validation accuracy
|
||||
|
||||
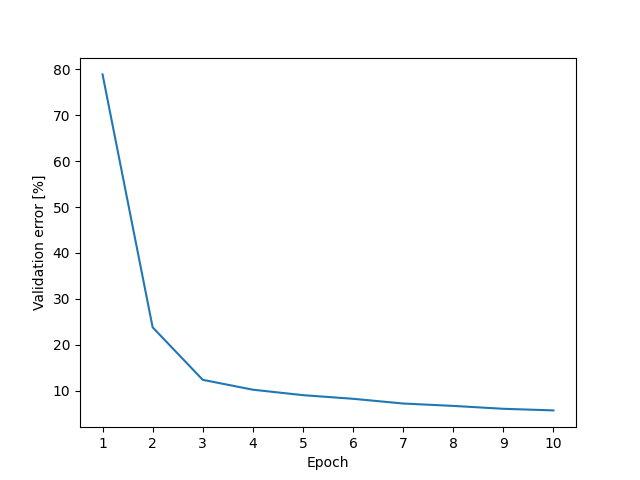
|
||||
|
||||
* Timing results using a P100 GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Preprocessing: 3.03 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
epoch batch train time [sec] validation accuracy
|
||||
1 97 10.07 0.2460
|
||||
2 194 18.60 0.7690
|
||||
3 291 27.13 0.8754
|
||||
4 388 35.65 0.8985
|
||||
5 485 44.18 0.9107
|
||||
6 582 52.70 0.9195
|
||||
7 679 61.23 0.9272
|
||||
8 776 69.75 0.9337
|
||||
9 873 78.28 0.9397
|
||||
10 970 86.81 0.9428
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Train time does not include preprocessing, evaluating validation accuracy or importing the pytorch library.
|
||||
|
||||
The total time, i.e. what `time python3 train.py` would report, was 42.125 and 103.699 seconds respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
* Timing results on a V100 GPU ([thanks to @ZipengFeng](https://github.com/99991/cifar10-fast-simple/issues/1#issuecomment-1057876448))
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Preprocessing: 4.78 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
epoch batch train time [sec] validation accuracy
|
||||
1 97 4.24 0.2051
|
||||
2 194 7.09 0.7661
|
||||
3 291 9.93 0.8749
|
||||
4 388 12.78 0.8982
|
||||
5 485 15.62 0.9139
|
||||
6 582 18.48 0.9237
|
||||
7 679 21.33 0.9301
|
||||
8 776 24.18 0.9348
|
||||
9 873 27.04 0.9396
|
||||
10 970 29.90 0.9422
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Timing results on an RTX 3060 Laptop GPU (6 GB VRAM)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Files already downloaded and verified
|
||||
Preprocessing: 4.67 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
epoch batch train time [sec] validation accuracy
|
||||
1 97 10.50 0.2578
|
||||
2 194 19.47 0.7549
|
||||
3 291 28.21 0.8737
|
||||
4 388 36.97 0.9013
|
||||
5 485 45.72 0.9127
|
||||
6 582 54.62 0.9213
|
||||
7 679 63.39 0.9286
|
||||
8 776 72.17 0.9348
|
||||
9 873 80.95 0.9395
|
||||
10 970 89.74 0.9412
|
||||
```
|
||||
BIN
cifar10-fast-simple/doc/a100_epoch_vs_validation_error.png
Normal file
BIN
cifar10-fast-simple/doc/a100_epoch_vs_validation_error.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 19 KiB |
28
cifar10-fast-simple/doc/plot.py
Normal file
28
cifar10-fast-simple/doc/plot.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
|||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
|
||||
result = """
|
||||
1 97 4.37 0.2109
|
||||
2 194 7.77 0.7620
|
||||
3 291 11.16 0.8764
|
||||
4 388 14.54 0.8979
|
||||
5 485 17.93 0.9098
|
||||
6 582 21.32 0.9177
|
||||
7 679 24.71 0.9280
|
||||
8 776 28.09 0.9332
|
||||
9 873 31.48 0.9395
|
||||
10 970 34.86 0.9430
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
rows = []
|
||||
for row in result.strip().split("\n"):
|
||||
numbers = [float(x) for x in row.split()]
|
||||
rows.append(numbers)
|
||||
|
||||
epoch, batch, t, accuracy = map(list, zip(*rows))
|
||||
|
||||
plt.plot(epoch, [100 - 100 * x for x in accuracy])
|
||||
plt.xticks(epoch)
|
||||
plt.xlabel("Epoch")
|
||||
plt.ylabel("Validation error [%]")
|
||||
plt.savefig("a100_epoch_vs_validation_error.png")
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
2006
cifar10-fast-simple/logs/A100.txt
Normal file
2006
cifar10-fast-simple/logs/A100.txt
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load diff
2006
cifar10-fast-simple/logs/P100.txt
Normal file
2006
cifar10-fast-simple/logs/P100.txt
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load diff
141
cifar10-fast-simple/model.py
Normal file
141
cifar10-fast-simple/model.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
|
|||
import torch
|
||||
import torch.nn as nn
|
||||
import torch.nn.functional as F
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def label_smoothing_loss(inputs, targets, alpha):
|
||||
log_probs = torch.nn.functional.log_softmax(inputs, dim=1, _stacklevel=5)
|
||||
kl = -log_probs.mean(dim=1)
|
||||
xent = torch.nn.functional.nll_loss(log_probs, targets, reduction="none")
|
||||
loss = (1 - alpha) * xent + alpha * kl
|
||||
return loss
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class GhostBatchNorm(nn.BatchNorm2d):
|
||||
def __init__(self, num_features, num_splits, **kw):
|
||||
super().__init__(num_features, **kw)
|
||||
|
||||
running_mean = torch.zeros(num_features * num_splits)
|
||||
running_var = torch.ones(num_features * num_splits)
|
||||
|
||||
self.weight.requires_grad = False
|
||||
self.num_splits = num_splits
|
||||
self.register_buffer("running_mean", running_mean)
|
||||
self.register_buffer("running_var", running_var)
|
||||
|
||||
def train(self, mode=True):
|
||||
if (self.training is True) and (mode is False):
|
||||
# lazily collate stats when we are going to use them
|
||||
self.running_mean = torch.mean(
|
||||
self.running_mean.view(self.num_splits, self.num_features), dim=0
|
||||
).repeat(self.num_splits)
|
||||
self.running_var = torch.mean(
|
||||
self.running_var.view(self.num_splits, self.num_features), dim=0
|
||||
).repeat(self.num_splits)
|
||||
return super().train(mode)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, input):
|
||||
n, c, h, w = input.shape
|
||||
if self.training or not self.track_running_stats:
|
||||
assert n % self.num_splits == 0, f"Batch size ({n}) must be divisible by num_splits ({self.num_splits}) of GhostBatchNorm"
|
||||
return F.batch_norm(
|
||||
input.view(-1, c * self.num_splits, h, w),
|
||||
self.running_mean,
|
||||
self.running_var,
|
||||
self.weight.repeat(self.num_splits),
|
||||
self.bias.repeat(self.num_splits),
|
||||
True,
|
||||
self.momentum,
|
||||
self.eps,
|
||||
).view(n, c, h, w)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return F.batch_norm(
|
||||
input,
|
||||
self.running_mean[: self.num_features],
|
||||
self.running_var[: self.num_features],
|
||||
self.weight,
|
||||
self.bias,
|
||||
False,
|
||||
self.momentum,
|
||||
self.eps,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def conv_bn_relu(c_in, c_out, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding=(1, 1)):
|
||||
return nn.Sequential(
|
||||
nn.Conv2d(c_in, c_out, kernel_size=kernel_size, padding=padding, bias=False),
|
||||
GhostBatchNorm(c_out, num_splits=16),
|
||||
nn.CELU(alpha=0.3),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def conv_pool_norm_act(c_in, c_out):
|
||||
return nn.Sequential(
|
||||
nn.Conv2d(c_in, c_out, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding=(1, 1), bias=False),
|
||||
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
|
||||
GhostBatchNorm(c_out, num_splits=16),
|
||||
nn.CELU(alpha=0.3),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def patch_whitening(data, patch_size=(3, 3)):
|
||||
# Compute weights from data such that
|
||||
# torch.std(F.conv2d(data, weights), dim=(2, 3))
|
||||
# is close to 1.
|
||||
h, w = patch_size
|
||||
c = data.size(1)
|
||||
patches = data.unfold(2, h, 1).unfold(3, w, 1)
|
||||
patches = patches.transpose(1, 3).reshape(-1, c, h, w).to(torch.float32)
|
||||
|
||||
n, c, h, w = patches.shape
|
||||
X = patches.reshape(n, c * h * w)
|
||||
X = X / (X.size(0) - 1) ** 0.5
|
||||
covariance = X.t() @ X
|
||||
|
||||
eigenvalues, eigenvectors = torch.linalg.eigh(covariance)
|
||||
|
||||
eigenvalues = eigenvalues.flip(0)
|
||||
|
||||
eigenvectors = eigenvectors.t().reshape(c * h * w, c, h, w).flip(0)
|
||||
|
||||
return eigenvectors / torch.sqrt(eigenvalues + 1e-2).view(-1, 1, 1, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ResNetBagOfTricks(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, first_layer_weights, c_in, c_out, scale_out):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
|
||||
c = first_layer_weights.size(0)
|
||||
|
||||
conv1 = nn.Conv2d(c_in, c, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
|
||||
conv1.weight.data = first_layer_weights
|
||||
conv1.weight.requires_grad = False
|
||||
|
||||
self.conv1 = conv1
|
||||
self.conv2 = conv_bn_relu(c, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), padding=0)
|
||||
self.conv3 = conv_pool_norm_act(64, 128)
|
||||
self.conv4 = conv_bn_relu(128, 128)
|
||||
self.conv5 = conv_bn_relu(128, 128)
|
||||
self.conv6 = conv_pool_norm_act(128, 256)
|
||||
self.conv7 = conv_pool_norm_act(256, 512)
|
||||
self.conv8 = conv_bn_relu(512, 512)
|
||||
self.conv9 = conv_bn_relu(512, 512)
|
||||
self.pool10 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=4, stride=4)
|
||||
self.linear11 = nn.Linear(512, c_out, bias=False)
|
||||
self.scale_out = scale_out
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
x = self.conv1(x)
|
||||
x = self.conv2(x)
|
||||
x = self.conv3(x)
|
||||
x = x + self.conv5(self.conv4(x))
|
||||
x = self.conv6(x)
|
||||
x = self.conv7(x)
|
||||
x = x + self.conv9(self.conv8(x))
|
||||
x = self.pool10(x)
|
||||
x = x.reshape(x.size(0), x.size(1))
|
||||
x = self.linear11(x)
|
||||
x = self.scale_out * x
|
||||
return x
|
||||
|
||||
Model = ResNetBagOfTricks
|
||||
278
cifar10-fast-simple/train.py
Normal file
278
cifar10-fast-simple/train.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,278 @@
|
|||
import time
|
||||
import copy
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import torch.nn as nn
|
||||
import torchvision
|
||||
import model
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def train(seed=0):
|
||||
# Configurable parameters
|
||||
epochs = 10
|
||||
batch_size = 512
|
||||
momentum = 0.9
|
||||
weight_decay = 0.256
|
||||
weight_decay_bias = 0.004
|
||||
ema_update_freq = 5
|
||||
ema_rho = 0.99 ** ema_update_freq
|
||||
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
|
||||
dtype = torch.float16 if device.type != "cpu" else torch.float32
|
||||
|
||||
# First, the learning rate rises from 0 to 0.002 for the first 194 batches.
|
||||
# Next, the learning rate shrinks down to 0.0002 over the next 582 batches.
|
||||
lr_schedule = torch.cat([
|
||||
torch.linspace(0e+0, 2e-3, 194),
|
||||
torch.linspace(2e-3, 2e-4, 582),
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
lr_schedule_bias = 64.0 * lr_schedule
|
||||
|
||||
# Print information about hardware on first run
|
||||
if seed == 0:
|
||||
if device.type == "cuda":
|
||||
print("Device :", torch.cuda.get_device_name(device.index))
|
||||
|
||||
print("Dtype :", dtype)
|
||||
print()
|
||||
|
||||
# Start measuring time
|
||||
start_time = time.perf_counter()
|
||||
|
||||
# Set random seed to increase chance of reproducability
|
||||
torch.manual_seed(seed)
|
||||
|
||||
# Setting cudnn.benchmark to True hampers reproducability, but is faster
|
||||
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
|
||||
|
||||
# Load dataset
|
||||
train_data, train_targets, valid_data, valid_targets = load_cifar10(device, dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
# Compute special weights for first layer
|
||||
weights = model.patch_whitening(train_data[:10000, :, 4:-4, 4:-4])
|
||||
|
||||
# Construct the neural network
|
||||
train_model = model.Model(weights, c_in=3, c_out=10, scale_out=0.125)
|
||||
|
||||
# Convert model weights to half precision
|
||||
train_model.to(dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
# Convert BatchNorm back to single precision for better accuracy
|
||||
for module in train_model.modules():
|
||||
if isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm2d):
|
||||
module.float()
|
||||
|
||||
# Upload model to GPU
|
||||
train_model.to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
# Collect weights and biases and create nesterov velocity values
|
||||
weights = [
|
||||
(w, torch.zeros_like(w))
|
||||
for w in train_model.parameters()
|
||||
if w.requires_grad and len(w.shape) > 1
|
||||
]
|
||||
biases = [
|
||||
(w, torch.zeros_like(w))
|
||||
for w in train_model.parameters()
|
||||
if w.requires_grad and len(w.shape) <= 1
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# Copy the model for validation
|
||||
valid_model = copy.deepcopy(train_model)
|
||||
|
||||
print(f"Preprocessing: {time.perf_counter() - start_time:.2f} seconds")
|
||||
|
||||
# Train and validate
|
||||
print("\nepoch batch train time [sec] validation accuracy")
|
||||
train_time = 0.0
|
||||
batch_count = 0
|
||||
for epoch in range(1, epochs + 1):
|
||||
# Flush CUDA pipeline for more accurate time measurement
|
||||
if torch.cuda.is_available():
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
|
||||
start_time = time.perf_counter()
|
||||
|
||||
# Randomly shuffle training data
|
||||
indices = torch.randperm(len(train_data), device=device)
|
||||
data = train_data[indices]
|
||||
targets = train_targets[indices]
|
||||
|
||||
# Crop random 32x32 patches from 40x40 training data
|
||||
data = [
|
||||
random_crop(data[i : i + batch_size], crop_size=(32, 32))
|
||||
for i in range(0, len(data), batch_size)
|
||||
]
|
||||
data = torch.cat(data)
|
||||
|
||||
# Randomly flip half the training data
|
||||
data[: len(data) // 2] = torch.flip(data[: len(data) // 2], [-1])
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(0, len(data), batch_size):
|
||||
# discard partial batches
|
||||
if i + batch_size > len(data):
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
# Slice batch from data
|
||||
inputs = data[i : i + batch_size]
|
||||
target = targets[i : i + batch_size]
|
||||
batch_count += 1
|
||||
|
||||
# Compute new gradients
|
||||
train_model.zero_grad()
|
||||
train_model.train(True)
|
||||
|
||||
logits = train_model(inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
loss = model.label_smoothing_loss(logits, target, alpha=0.2)
|
||||
|
||||
loss.sum().backward()
|
||||
|
||||
lr_index = min(batch_count, len(lr_schedule) - 1)
|
||||
lr = lr_schedule[lr_index]
|
||||
lr_bias = lr_schedule_bias[lr_index]
|
||||
|
||||
# Update weights and biases of training model
|
||||
update_nesterov(weights, lr, weight_decay, momentum)
|
||||
update_nesterov(biases, lr_bias, weight_decay_bias, momentum)
|
||||
|
||||
# Update validation model with exponential moving averages
|
||||
if (i // batch_size % ema_update_freq) == 0:
|
||||
update_ema(train_model, valid_model, ema_rho)
|
||||
|
||||
if torch.cuda.is_available():
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
|
||||
# Add training time
|
||||
train_time += time.perf_counter() - start_time
|
||||
|
||||
valid_correct = []
|
||||
for i in range(0, len(valid_data), batch_size):
|
||||
valid_model.train(False)
|
||||
|
||||
# Test time agumentation: Test model on regular and flipped data
|
||||
regular_inputs = valid_data[i : i + batch_size]
|
||||
flipped_inputs = torch.flip(regular_inputs, [-1])
|
||||
|
||||
logits1 = valid_model(regular_inputs).detach()
|
||||
logits2 = valid_model(flipped_inputs).detach()
|
||||
|
||||
# Final logits are average of augmented logits
|
||||
logits = torch.mean(torch.stack([logits1, logits2], dim=0), dim=0)
|
||||
|
||||
# Compute correct predictions
|
||||
correct = logits.max(dim=1)[1] == valid_targets[i : i + batch_size]
|
||||
|
||||
valid_correct.append(correct.detach().type(torch.float64))
|
||||
|
||||
# Accuracy is average number of correct predictions
|
||||
valid_acc = torch.mean(torch.cat(valid_correct)).item()
|
||||
|
||||
print(f"{epoch:5} {batch_count:8d} {train_time:19.2f} {valid_acc:22.4f}")
|
||||
|
||||
return valid_acc
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess_data(data, device, dtype):
|
||||
# Convert to torch float16 tensor
|
||||
data = torch.tensor(data, device=device).to(dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
# Normalize
|
||||
mean = torch.tensor([125.31, 122.95, 113.87], device=device).to(dtype)
|
||||
std = torch.tensor([62.99, 62.09, 66.70], device=device).to(dtype)
|
||||
data = (data - mean) / std
|
||||
|
||||
# Permute data from NHWC to NCHW format
|
||||
data = data.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
return data
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def load_cifar10(device, dtype, data_dir="~/data"):
|
||||
train = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root=data_dir, download=True)
|
||||
valid = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root=data_dir, train=False)
|
||||
|
||||
train_data = preprocess_data(train.data, device, dtype)
|
||||
valid_data = preprocess_data(valid.data, device, dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
train_targets = torch.tensor(train.targets).to(device)
|
||||
valid_targets = torch.tensor(valid.targets).to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
# Pad 32x32 to 40x40
|
||||
train_data = nn.ReflectionPad2d(4)(train_data)
|
||||
|
||||
return train_data, train_targets, valid_data, valid_targets
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def update_ema(train_model, valid_model, rho):
|
||||
# The trained model is not used for validation directly. Instead, the
|
||||
# validation model weights are updated with exponential moving averages.
|
||||
train_weights = train_model.state_dict().values()
|
||||
valid_weights = valid_model.state_dict().values()
|
||||
for train_weight, valid_weight in zip(train_weights, valid_weights):
|
||||
if valid_weight.dtype in [torch.float16, torch.float32]:
|
||||
valid_weight *= rho
|
||||
valid_weight += (1 - rho) * train_weight
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def update_nesterov(weights, lr, weight_decay, momentum):
|
||||
for weight, velocity in weights:
|
||||
if weight.requires_grad:
|
||||
gradient = weight.grad.data
|
||||
weight = weight.data
|
||||
|
||||
gradient.add_(weight, alpha=weight_decay).mul_(-lr)
|
||||
velocity.mul_(momentum).add_(gradient)
|
||||
weight.add_(gradient.add_(velocity, alpha=momentum))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def random_crop(data, crop_size):
|
||||
crop_h, crop_w = crop_size
|
||||
h = data.size(2)
|
||||
w = data.size(3)
|
||||
x = torch.randint(w - crop_w, size=(1,))[0]
|
||||
y = torch.randint(h - crop_h, size=(1,))[0]
|
||||
return data[:, :, y : y + crop_h, x : x + crop_w]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def sha256(path):
|
||||
import hashlib
|
||||
with open(path, "rb") as f:
|
||||
return hashlib.sha256(f.read()).hexdigest()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def getrelpath(abspath):
|
||||
import os
|
||||
return os.path.relpath(abspath, os.getcwd())
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def print_info():
|
||||
# Knowing this information might improve chance of reproducability
|
||||
print("File :", getrelpath(__file__), sha256(__file__))
|
||||
print("Model :", getrelpath(model.__file__), sha256(model.__file__))
|
||||
print("PyTorch:", torch.__version__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
print_info()
|
||||
|
||||
accuracies = []
|
||||
threshold = 0.94
|
||||
for run in range(100):
|
||||
valid_acc = train(seed=run)
|
||||
accuracies.append(valid_acc)
|
||||
|
||||
# Print accumulated results
|
||||
within_threshold = sum(acc >= threshold for acc in accuracies)
|
||||
acc = threshold * 100.0
|
||||
print()
|
||||
print(f"{within_threshold} of {run + 1} runs >= {acc} % accuracy")
|
||||
mean = sum(accuracies) / len(accuracies)
|
||||
variance = sum((acc - mean)**2 for acc in accuracies) / len(accuracies)
|
||||
std = variance**0.5
|
||||
print(f"Min accuracy: {min(accuracies)}")
|
||||
print(f"Max accuracy: {max(accuracies)}")
|
||||
print(f"Mean accuracy: {mean} +- {std}")
|
||||
print()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in a new issue